Anyone who uses doctor blades for printing knows the range of options available today. From the thickness of the material to the tip configuration, a doctor blade’s design has a direct impact on the job it will do. While traditional tip options have ranged from straight to rounded to lamella, the new kid on the block, “MicroTip,” offers printers a smart choice when applying special effects coating.
Special effects coatings are challenging
More and more, packaging companies are using specialty coatings to differentiate their brands and create a tactile and visual experience for consumers. However, special coatings such as glitter, grit, soft-touch, metallics and pearlescents present particular challenges for the printer. These coatings have high viscosities and contain larger particles which make it difficult to accurately control the amount of coating
being applied. (UV chemistries, common in specialty coating applications, have a viscosity of 5-7 times that of water and solvent-based formulas.) This higher viscosity applies extra pressure to the metering blade, resulting in hydroplaning or “spitting” (especially at high line speeds), and increases coating consumption and waste. In these cases, a customized blade solution is often necessary to control the lay-down of coating.
New Polymer Doctor Blades with MicroTips can help
Doctor blade manufacturers have found a way to make new polymer doctor blade materials that can overcome the limitations of steel in specialty coating applications. By engineering a modified lamella tip, known as a “MicroTip”, on these materials, they have introduced a doctor blade product that offers the best of traditional plastic and steel.
Why do they work?
When used to apply special effects coating, steel blades are subject to accelerated blade wear from the coarse anilox engravings and corrosion from the harsh coating chemistries. Today’s new polymer materials are compatible with all coating formulas and do what plastic blades are known to do best: last longer.
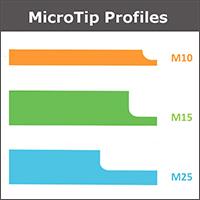
 The blades can be engineered to a full range of size and profile combinations to optimize metering performance with the higher viscosity and large particulate formulas. They range in thickness from .027”/.7mm to .050”/1.25mm to offer varying degrees of stiffness, rigidity and deflection. These properties combined with the new MicroTip edge allow the blades to achieve a fine contact area with the anilox roll and deliver a fluid transfer of coating to the blanket with no spitting or slinging, even at high press speeds. Add to this a range of MicroTips, (M10, M15 and M25) and these blades can be customized for a “perfect fit.”
The blades can be engineered to a full range of size and profile combinations to optimize metering performance with the higher viscosity and large particulate formulas. They range in thickness from .027”/.7mm to .050”/1.25mm to offer varying degrees of stiffness, rigidity and deflection. These properties combined with the new MicroTip edge allow the blades to achieve a fine contact area with the anilox roll and deliver a fluid transfer of coating to the blanket with no spitting or slinging, even at high press speeds. Add to this a range of MicroTips, (M10, M15 and M25) and these blades can be customized for a “perfect fit.”
Doctor blade optimization for special effects coating
The choice of blade thickness and tip will be determined by the anilox configuration, which is driven by the viscosity and solid load of the coating. Typically, higher line screens and lower cell volumes will require a smaller MicroTip (an M10 or M15 for dull/satin/gloss coatings for example), but as line screens decline and volumes increase, a MicroTip providing a larger contact area (M15 or M25) will perform better. By optimizing their next generation polymer doctor blades with the appropriate MicroTip, printers are able to achieve longer blade life in these applications than with steel.
If you’re a printer struggling with special effects coating, consider switching to a next generation polymer doctor blade with a MicroTip. A magical combination of advanced material and tip might be just what you need to achieve a perfect lay-down of coating with longer blade life to boot.